Blood Circulation on Vertebrate
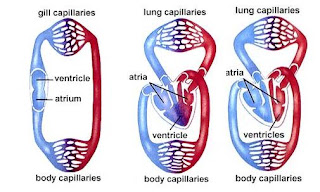
Human, birds and mammals have 4 chambered heart that completely separate oxygen rich and oxygen depleted blood. Fish have 2 chambered heart in which a single loop circulatory pattern takes blood from the heart to the gills and then to the body. Amphibian have 3 chambered heart with two atria and one ventricle. A loop from the heart goes to the pulmonary capillary beds, where gas exchange occurs. Blood then is returned to the heart. Blood existing the ventricle is diverted, some to the pulmonary circuit, some to systemic circuit. The disadvantage of the three chambered heart is the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. Some reptiles have partial separation of the ventricle. Other reptiles, plus, all birds and mammals, have a 4 chambered heart, with complete separation of both systemic and pulmonary circuits.
The three of blood circulation systems are on fish (left), on amphibian (center) and on bird/mammal (right).
Circulatory systems of several vertebrates are showing the progressive evolution of the four chambered heart.
The human heart is a two sided, 4 chambered structured with muscular walls. The heart beats or contracts 70 times per minute. The human heart will undergo over 3 billion contraction cycles during a normal lifetime. The cardiac cycle consists of two parts; systole (contraction of the heart muscle) and diastole (relaxation of the heart muscle). Atria contract while ventricle relax. The pulse is a wave of contraction transmitted along the arteries. Valve in the heart open and close during the cardiac cycle. Heart muscle contraction is due to the presence of nodal tissue in two regions of the heart.
Other blood articles:
The three of blood circulation systems are on fish (left), on amphibian (center) and on bird/mammal (right).
Circulatory systems of several vertebrates are showing the progressive evolution of the four chambered heart.
The human heart is a two sided, 4 chambered structured with muscular walls. The heart beats or contracts 70 times per minute. The human heart will undergo over 3 billion contraction cycles during a normal lifetime. The cardiac cycle consists of two parts; systole (contraction of the heart muscle) and diastole (relaxation of the heart muscle). Atria contract while ventricle relax. The pulse is a wave of contraction transmitted along the arteries. Valve in the heart open and close during the cardiac cycle. Heart muscle contraction is due to the presence of nodal tissue in two regions of the heart.
Other blood articles: